Appearance
服务熔断与降级
在微服务架构中,服务之间存在复杂的依赖关系。当一个服务出现故障时,可能会导致依赖它的服务也出现故障,最终造成故障的级联传播,这就是著名的"雪崩效应"。服务熔断和降级是微服务架构中应对这种情况的关键韧性模式。
服务熔断与降级概念
服务熔断(Circuit Breaking)
服务熔断类似于电路保护中的断路器:当检测到系统中某个服务持续出现故障时(如请求超时、异常比率过高),熔断器会"跳闸",阻止对该服务的后续请求,从而保护服务调用方和被调用方。
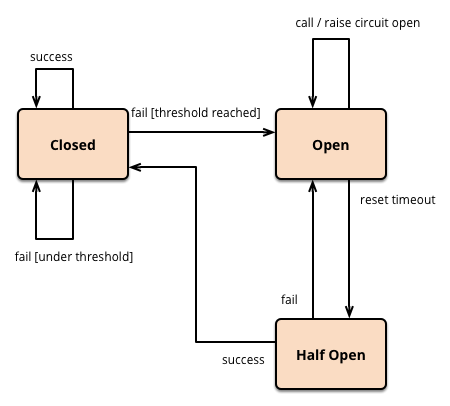
熔断器通常有三种状态:
- 关闭(Closed):默认状态,请求正常通过
- 打开(Open):熔断激活状态,阻止所有请求,直接返回失败或降级响应
- 半开(Half-Open):尝试恢复状态,允许部分请求通过,如果成功则转为关闭状态,否则重新回到打开状态
服务降级(Fallback)
当服务调用失败或熔断器打开时,系统应该提供一种替代方案,这就是服务降级。降级通常包括:
- 返回缺省值或缓存数据
- 提供简化功能
- 暂时禁用非核心功能
- 返回友好的错误信息
服务降级的目的是保证核心业务流程的可用性,即使在非理想条件下,也能提供可接受的用户体验。
Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker
Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker 是 Spring Cloud 提供的服务熔断抽象,它为不同的熔断器实现提供了统一的编程模型。目前支持的实现包括:
- Netflix Hystrix (已进入维护模式)
- Resilience4j
- Spring Retry
- Alibaba Sentinel
Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker 基本使用
Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker 提供了一个简单统一的 API,使开发者可以轻松实现服务熔断和降级。
引入依赖
根据选择的熔断器实现引入相应的依赖,以 Resilience4j 为例:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-circuitbreaker-resilience4j</artifactId>
</dependency>创建熔断器工厂
Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker 提供了 CircuitBreakerFactory 接口,可以创建和配置熔断器:
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
private final CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
public ProductService(RestTemplate restTemplate, CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
this.circuitBreakerFactory = circuitBreakerFactory;
}
public Product getProductById(String productId) {
return circuitBreakerFactory.create("getProduct")
.run(() -> {
// 调用产品服务的代码
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/products/{id}", Product.class, productId);
}, throwable -> {
// 降级逻辑
return getDefaultProduct(productId);
});
}
private Product getDefaultProduct(String productId) {
Product fallback = new Product();
fallback.setId(productId);
fallback.setName("Temporary Unavailable");
fallback.setDescription("The product information is temporarily unavailable. Please try again later.");
fallback.setPrice(0.0);
return fallback;
}
}在上面的例子中:
create("getProduct")创建一个名为 "getProduct" 的熔断器run()方法的第一个参数是要执行的主要逻辑run()方法的第二个参数是降级逻辑,当主要逻辑失败或熔断器打开时执行
熔断器实现
1. Netflix Hystrix
Hystrix 是 Netflix 开源的熔断器库,虽然已进入维护模式,但在很多项目中仍在使用。
添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>启用 Hystrix
java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}使用 @HystrixCommand 注解
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ProductService(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "getDefaultProduct",
commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "4"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds", value = "10000"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "50"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds", value = "1000")
})
public Product getProductById(String productId) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/products/{id}", Product.class, productId);
}
public Product getDefaultProduct(String productId, Throwable throwable) {
Product fallback = new Product();
fallback.setId(productId);
fallback.setName("Temporary Unavailable");
fallback.setDescription("Error: " + throwable.getMessage());
fallback.setPrice(0.0);
return fallback;
}
}在上面的配置中:
circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold:触发熔断的最小请求数circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds:熔断后多久进入半开状态circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage:错误率阈值,超过后触发熔断execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds:超时时间
Hystrix Dashboard
Hystrix Dashboard 是一个可视化工具,用于监控 Hystrix 指标:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}2. Resilience4j
Resilience4j 是一个轻量级的容错库,受 Hystrix 启发,但专为 Java 8 和 函数式编程设计。它是 Hystrix 的推荐替代品。
添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-circuitbreaker-resilience4j</artifactId>
</dependency>基本配置
java
@Configuration
public class Resilience4jConfig {
@Bean
public Customizer<Resilience4jCircuitBreakerFactory> defaultCustomizer() {
// 创建断路器配置
CircuitBreakerConfig circuitBreakerConfig = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50) // 失败率阈值
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofMillis(1000)) // 断路器打开持续时间
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(2) // 半开状态允许通过的请求数
.slidingWindowSize(10) // 滑动窗口大小
.build();
// 创建超时配置
TimeLimiterConfig timeLimiterConfig = TimeLimiterConfig.custom()
.timeoutDuration(Duration.ofSeconds(4)) // 超时时间
.build();
return factory -> factory.configureDefault(id -> new Resilience4JConfigBuilder(id)
.circuitBreakerConfig(circuitBreakerConfig)
.timeLimiterConfig(timeLimiterConfig)
.build());
}
}使用 CircuitBreaker 注解
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ProductService(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
@CircuitBreaker(name = "productService", fallbackMethod = "getDefaultProduct")
public Product getProductById(String productId) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/products/{id}", Product.class, productId);
}
public Product getDefaultProduct(String productId, Exception e) {
Product fallback = new Product();
fallback.setId(productId);
fallback.setName("Temporary Unavailable");
fallback.setDescription("Error: " + e.getMessage());
fallback.setPrice(0.0);
return fallback;
}
}Resilience4j 高级特性
除了熔断器外,Resilience4j 还提供了其他容错模式:
- 重试(Retry):当操作失败时自动重试
java
@Retry(name = "retryService", fallbackMethod = "fallbackMethod")
public String serviceWithRetry() {
// 可能失败的服务调用
}- 舱壁(Bulkhead):限制并发调用数量
java
@Bulkhead(name = "bulkheadService", fallbackMethod = "fallbackMethod")
public String serviceWithBulkhead() {
// 限制并发数的服务调用
}- 限流(RateLimiter):限制对服务的请求速率
java
@RateLimiter(name = "rateLimiterService", fallbackMethod = "fallbackMethod")
public String serviceWithRateLimiter() {
// 限制请求率的服务调用
}- 超时(TimeLimiter):设置操作的超时时间
java
@TimeLimiter(name = "timeLimiterService", fallbackMethod = "fallbackMethod")
public CompletableFuture<String> serviceWithTimeLimiter() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(this::slowOperation);
}这些注解可以组合使用,提供全面的服务保护策略:
java
@CircuitBreaker(name = "backendA", fallbackMethod = "fallback")
@RateLimiter(name = "backendA")
@Bulkhead(name = "backendA")
@Retry(name = "backendA")
public String serviceCall() {
return restTemplate.getForObject("/some-url", String.class);
}3. Spring Retry
Spring Retry 是针对可重试操作的轻量级框架,适用于偶发性故障的场景。
添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>启用重试功能
java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableRetry
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}使用 @Retryable 注解
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ProductService(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
@Retryable(value = {RestClientException.class}, maxAttempts = 3, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000))
public Product getProductById(String productId) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/products/{id}", Product.class, productId);
}
@Recover
public Product recover(RestClientException e, String productId) {
Product fallback = new Product();
fallback.setId(productId);
fallback.setName("Temporary Unavailable");
fallback.setDescription("The product is unavailable due to service issues.");
fallback.setPrice(0.0);
return fallback;
}
}在上面的配置中:
value指定要重试的异常类型maxAttempts指定最大重试次数backoff指定重试间隔@Recover注解的方法在重试失败后执行
4. Alibaba Sentinel
Sentinel 是阿里巴巴开源的面向分布式服务架构的流量控制组件,提供了熔断降级、流量控制等功能。
添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>配置 Sentinel
yaml
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
eager: true使用 @SentinelResource 注解
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ProductService(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
@SentinelResource(value = "getProductById", fallback = "getDefaultProduct")
public Product getProductById(String productId) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/products/{id}", Product.class, productId);
}
public Product getDefaultProduct(String productId, Throwable throwable) {
Product fallback = new Product();
fallback.setId(productId);
fallback.setName("Temporary Unavailable");
fallback.setDescription("Error: " + throwable.getMessage());
fallback.setPrice(0.0);
return fallback;
}
}Sentinel 还支持通过 Dashboard 进行动态规则配置:
- 流量控制规则
- 熔断降级规则
- 系统保护规则
- 热点参数规则
- 授权规则
熔断降级的最佳实践
设计原则
- 故障隔离:使用舱壁模式隔离依赖服务的故障
- 快速失败:快速检测并响应故障,避免长时间阻塞
- 优雅降级:提供合理的降级策略,保持核心功能可用
- 自动恢复:系统应能自动从故障中恢复
熔断器配置建议
- 合理的阈值设置:错误率阈值应根据业务容忍度设置,通常在 40%-60% 之间
- 足够的采样窗口:采样窗口不宜过小,否则可能导致误判
- 适当的恢复时间:熔断后的恢复时间应足够长,给依赖服务足够的恢复时间
- 智能的降级策略:降级策略应根据业务特点设计,尽量返回有意义的信息
监控和告警
- 实时监控熔断状态:监控熔断器的状态变化和触发情况
- 统计服务调用指标:记录成功率、响应时间、吞吐量等关键指标
- 设置合理的告警阈值:当熔断频繁触发时应及时告警
- 分析故障根源:建立故障分析流程,快速响应和解决问题
测试策略
- 混沌测试:模拟依赖服务故障,验证熔断降级机制的有效性
- 性能测试:验证系统在高负载下熔断降级机制的表现
- 恢复测试:验证系统在依赖服务恢复后的自动恢复能力
- 配置测试:测试不同熔断器参数配置下系统的行为
实战案例
下面是一个电商系统中使用服务熔断降级的案例:
系统架构
- 商品服务:提供商品信息
- 库存服务:管理商品库存
- 订单服务:处理订单创建和管理
- 支付服务:处理支付相关业务
- 用户服务:管理用户信息
商品详情页面场景
在商品详情页面,需要调用多个微服务:
java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProductDetailService {
private final ProductClient productClient;
private final InventoryClient inventoryClient;
private final ReviewClient reviewClient;
private final RecommendationClient recommendationClient;
private final CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
public ProductDetailService(ProductClient productClient,
InventoryClient inventoryClient,
ReviewClient reviewClient,
RecommendationClient recommendationClient,
CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory) {
this.productClient = productClient;
this.inventoryClient = inventoryClient;
this.reviewClient = reviewClient;
this.recommendationClient = recommendationClient;
this.circuitBreakerFactory = circuitBreakerFactory;
}
public ProductDetailDTO getProductDetail(String productId) {
ProductDetailDTO detail = new ProductDetailDTO();
// 获取商品基本信息(核心功能,无降级)
Product product = productClient.getProductById(productId);
detail.setProduct(product);
// 获取库存信息(核心功能,降级为缺省值)
CircuitBreaker inventoryCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("inventory");
InventoryDTO inventory = inventoryCB.run(
() -> inventoryClient.getInventory(productId),
throwable -> {
log.error("Inventory service error", throwable);
InventoryDTO fallback = new InventoryDTO();
fallback.setProductId(productId);
fallback.setAvailable(false);
fallback.setMessage("Inventory information temporarily unavailable");
return fallback;
}
);
detail.setInventory(inventory);
// 获取商品评论(非核心功能,可完全降级)
CircuitBreaker reviewCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("review");
List<ReviewDTO> reviews = reviewCB.run(
() -> reviewClient.getReviewsForProduct(productId),
throwable -> {
log.error("Review service error", throwable);
return Collections.emptyList();
}
);
detail.setReviews(reviews);
// 获取推荐商品(非核心功能,可完全降级)
CircuitBreaker recommendationCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("recommendation");
List<Product> recommendations = recommendationCB.run(
() -> recommendationClient.getRecommendationsForProduct(productId),
throwable -> {
log.error("Recommendation service error", throwable);
return Collections.emptyList();
}
);
detail.setRecommendations(recommendations);
return detail;
}
}订单创建场景
订单创建涉及多个服务的协作,需要仔细处理熔断降级:
java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
private final ProductClient productClient;
private final InventoryClient inventoryClient;
private final PaymentClient paymentClient;
private final CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
// 构造函数注入...
@Transactional
public OrderDTO createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 1. 检查商品信息(必须成功)
CircuitBreaker productCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("product");
Product product = productCB.run(
() -> productClient.getProductById(request.getProductId()),
throwable -> {
log.error("Cannot retrieve product information: {}", throwable.getMessage());
throw new OrderCreationException("Product information unavailable, cannot create order");
}
);
// 2. 检查库存(必须成功)
CircuitBreaker inventoryCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("inventory");
boolean inventoryAvailable = inventoryCB.run(
() -> inventoryClient.checkAndReserveInventory(request.getProductId(), request.getQuantity()),
throwable -> {
log.error("Cannot check inventory: {}", throwable.getMessage());
throw new OrderCreationException("Inventory service unavailable, cannot create order");
}
);
if (!inventoryAvailable) {
throw new InsufficientInventoryException("Not enough inventory for product: " + request.getProductId());
}
// 3. 创建订单(本地操作)
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
order.setAmount(product.getPrice() * request.getQuantity());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.CREATED);
orderRepository.save(order);
// 4. 处理支付(可降级,用户可以稍后支付)
CircuitBreaker paymentCB = circuitBreakerFactory.create("payment");
PaymentResult paymentResult = paymentCB.run(
() -> paymentClient.processPayment(order.getId(), order.getAmount()),
throwable -> {
log.error("Payment service error: {}", throwable.getMessage());
PaymentResult fallback = new PaymentResult();
fallback.setOrderId(order.getId());
fallback.setSuccess(false);
fallback.setMessage("Payment service temporarily unavailable. Please try payment later.");
return fallback;
}
);
// 5. 更新订单状态
if (paymentResult.isSuccess()) {
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.PAID);
} else {
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.AWAITING_PAYMENT);
order.setPaymentMessage(paymentResult.getMessage());
}
orderRepository.save(order);
// 6. 返回订单信息
return convertToDTO(order);
}
private OrderDTO convertToDTO(Order order) {
// 转换逻辑...
}
}这个例子展示了以下最佳实践:
- 区分核心功能和非核心功能,对它们应用不同的降级策略
- 为不同的服务调用使用不同的熔断器,避免一个服务故障影响其他服务
- 提供有意义的错误信息和降级行为
- 记录详细的错误日志,便于问题排查
总结
服务熔断和降级是微服务架构中保障系统韧性的关键技术。Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker 提供了统一的抽象,使开发者可以根据需求选择不同的熔断器实现。
通过合理配置熔断器和设计降级策略,可以防止故障蔓延,提高系统的可用性和稳定性。在实践中,应该根据业务重要性和依赖关系,为不同的服务调用设置适当的熔断降级策略,并持续监控系统行为,及时调整配置参数。
在实践中,熔断降级不应该被视为一种事后补救措施,而应该作为系统设计的一部分,从一开始就纳入考虑。通过合理配置熔断参数、设计降级策略、监控和测试,可以构建出具有高可用性和韧性的微服务系统。